|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Generic search/Exact-match search
- Search performed on a key item or on a non-key item
- Performing a search on a composite key
- Search on an array item
- Search and filter
- Looping through records that match a condition
- Exact-match search in Access
- Locks
- Optimizing iterations
- Native XML Connector
<Source>.ReadSeekFirst (Function) In french: <Source>.LitRecherchePremier
 Not available with this kind of connection Not available with this kind of connection
Positions on the first record of a data file whose value for a specific item is strictly equal to a sought value (exact-match search). The record is read and the corresponding HFSQL variables are updated. In most cases, <Source>.ReadSeekFirst sets the position in the data file to loop through the records that match a condition. <Source>.ReadNext is used to read the next record corresponding to the condition. Several cases may occur after the call to <Source>.ReadSeekFirst: - a Record corresponding to the condition has been foundblocked (if necessary) and loaded into memory: function <Source>.Found returns True.
- if there is no record corresponding to the condition, but if a record with a higher value exists the record is read, function <Source>.Out returns False and function <Source>.Found returns False.
- the data file is empty no reading is performed, function <Source>.Out returns True and function <Source>.Found returns False.
- the function attempts to block a record already blocked for playback: no playback is performed, function HErrorLock returns True and function <Source>.Out returns True.
Note: By default, a automatic management of lock errors and modification conflicts is performed (except in stored procedure code).. This assisted management of errors can be customized or disabled at any time by <Source>.OnError.
<Source>.ReadSeekFirst can be used with the data files, HFSQL views or queries.
Client.LitRecherchePremier(Nom, "DUPOND")
IF Client.Trouve() = False THEN
Error("Client non trouvé")
RETURN
ELSE
END
Syntax
<Result> = <Source>.ReadSeekFirst(<Item> , <Search value> [, <Options>])
<Result>: Boolean - True if the record was found (corresponds to the value returned by <Source>.Found).
- False if a problem occurs. This problem can be caused by:
- or a positioning problem (empty data file, etc.): function <Source>.Found returns False and function HError returns 0.
- an error: HError returns an integer other than 0. HErrorInfo returns more details.
<Source>: Type corresponding to the specified source Name of the HFSQL data file, view or query used. <Item>: Character string Name of item on which the search will be performed. This item can be a search key or not.
<Search value>: Type corresponding to the value Value of the sought item. <Options>: Optional constant (or combination of constants) Used to configure:- the lock mode applied to the sought record
- the type of search performed.
| | | hForwardOnly | | | hGeneric | Generic search (see the Notes)
An exact-match search is performed by default (constant not specified). | | hKeepFilter | The filter set by <Source>.Filter will be taken into account, even if the search key is not optimized for the filter. Reminder: <Source>.Filter returns the optimized search key for the filter.
Caution: in this case, on large data files, performance problems may occur..
By default, the iteration performed after <Source>.ReadSeekFirst ignores the filter. | | hLimitParsing | The iteration will stop when the last search value is found or if no value matches the search.
The current record will correspond to this last record found.
<Source>.Found will return False and <Source>.Out will return True.
This constant is used to optimize search speed in Client/Server mode and on external databases (accessed via OLE DB or via Native Connectors). | | hLockNo | No blocking: the Record can be played back or modified by another application during playback.
| | hLockReadWrite | Read/write lock: the record being read cannot be read or modified by another application.
The lock mode is ignored if a query is used.
| | hLockWrite | Write lock: the record currently read can be read by another application but it cannot be modified by another application.
The lock mode is ignored if a query is used.
| | hNoRefresh | |
Remarks Generic search/Exact-match search - Generic search (mainly for string fields): Finds all records beginning with the specified value.
For example: When performing a generic search for the string "Martin" in the NAME field, all records whose Name field begins with "Martin" will match the search. Therefore, the record that contains "Smither" will match the search (<Source>.Found returns True).
Note: For compatibility with WINDEV 5.5, the generic search for an empty string ("") is equivalent to using the <Source>.ReadFirst function. - Exact-match search: Finds all records exactly matching the specified value.
For example: When performing an exact-match search on the string "Martin" for the field NAME, function <Source>.Found returns True only for records where the heading is exactly "Martin". - Examples of searches on the CUSTOMER data file sorted by name:
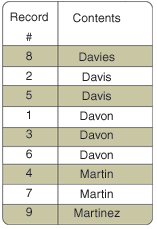 | | | | | | | Search value | Options | <Source>.ReadSeekFirst sets the position on the record. | <Source>.Found returns | <Source>.Out returns | Explanations | | Davon | | 1 | True | False | Davon exists.
The end of data file was not reached yet. | | Davo | | 1 | False | False | Davo does not exist. Position on the first greater value (Davon).
The end of data file was not reached yet. | | Moor | hGeneric | 8 | True | False | Moor does not exist but the search is a generic search and Moore is found (among others).
The end of data file was not reached yet. | | Moor | | The record was not found (no move, the current record does not change). | False | False | Moor does not exist.
The end of data file was not reached yet. | | Norbert | | The record was not found (no move, the current record does not change). | False | True | Norbert does not exist.
Set to the first higher value (this value does not exist): the end of the data file is reached. |
For more details, see the Hyper File 5.5 and 7: How are blank spaces handled in searches? table Search performed on a key item or on a non-key item The search can be performed on a key item or a non-key item. If the search is performed on a key item: - the search is fast and the result is sorted.
- if the iteration operation is continued by <Source>.ReadNext, the next records will correspond to the values greater than or equal to the search value. In this case, <Source>.Out must be checked after each read operation to find out whether the end of the data file has been reached.
If the search is performed on a non-key item: Performing a search on a composite key Several methods can be used to perform a search on a composite key: 1. Using a list of values The following syntax is used to perform a search on a composite key: HReadSeekFirst(<File Name>, <Name of Composite Key>,
[<Search value of first element of composite key>,
<Search value of first element of composite key>, ...]) Example:
Client.LitRecherchePremier(Nom_Prénom, ["MOULIN", "Françoise"])
Example:
bufValRech is Buffer = Client.ConstruitValClé(Nom_Prénom, sNom, sPrénom)
Client.RecherchePremier(Nom_Prénom, bufValRech)
WHILE Client.Trouve()
Client.Supprime()
Client.Suivant(Nom_Prénom)
END
Search on an array item The search is performed on the first array element (element with index 1). To perform a search on the other array elements, use the filters or queries. Search and filter If a filter is enabled ( <Source>.Filter), the filter is taken into account by the search only if the key used is identical. To apply this filter in the rest of the iteration (even if the search key is not optimized for the filter), use the hKeepFilter constant.
Looping through records that match a condition In most cases, <Source>.ReadSeekFirst sets the position in the data file to loop through the records that match a condition. <Source>.ReadNext and <Source>.ReadPrevious are used to read the next and previous matching records. To ignore the search while going to the next or previous record, use one of the following functions:
This page is also available for…
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|